Price from (last known)
£32,945
| Availability |
Not available to order |
| Available to order from |
June 2019 |
| Available to order until |
March 2022 |
| Annual VED |
£0 |
| Congestion Charge |
£0 |
| Insurance Group |
21 |
Price shown is the last known On The Road price: it includes VAT, first year VED, vehicle first registration fee, number plates and delivery.
Real Range between 150 - 315 mi
| City - Cold Weather |
210 mi |
| Highway - Cold Weather |
150 mi |
| Combined - Cold Weather |
180 mi |
| City - Mild Weather |
315 mi |
| Highway - Mild Weather |
195 mi |
| Combined - Mild Weather |
245 mi |
Indication of real-world range in several situations. Cold weather: 'worst-case' based on -10°C and use of heating. Mild weather: 'best-case' based on 23°C and no use of A/C. For 'Highway' figures a constant speed of 70 mph is assumed. The actual range will depend on speed, style of driving, weather and route conditions.
Battery
| Nominal Capacity |
62.0 kWh |
| Battery Type |
Lithium-ion |
| Number of Cells |
288 |
| Architecture |
400 V |
| Warranty Period |
8 years |
| Warranty Mileage |
100,000 mi |
| Useable Capacity* |
59.0 kWh |
| Cathode Material |
NCM523 |
| Pack Configuration |
96s3p |
| Nominal Voltage |
350 V |
| Form Factor |
No Data |
| Name / Reference |
No Data |
Charging
Home / Destination
| Charge Port |
Type 2 |
| Port Location |
Front Side - Middle |
| Charge Power |
6.6 kW AC |
| Charge Time (0->215 mi) |
10h45m |
| Charge Speed |
20 mph |
Rapid Charging
| Fastcharge Port |
CHAdeMO |
| FC Port Location |
Front Side - Middle |
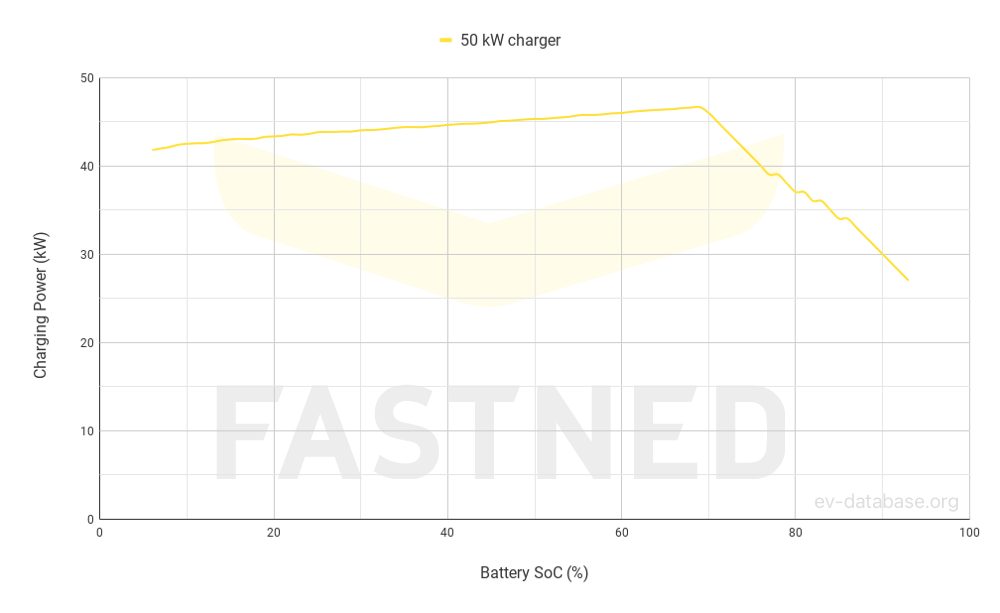
| Fastcharge Power (max) |
46 kW DC |
| Fastcharge Power (10-80%) |
44 kW DC |
| Fastcharge Time (21->172 mi) |
59 min |
| Fastcharge Speed |
150 mph |
| Autocharge Supported |
No |
Plug & Charge
| Plug & Charge Supported |
No |
Bidirectional Charging (V2X / BPT)
Vehicle-to-Load (V2L)
| V2L Supported |
No |
| Max. Output Power |
- |
| Exterior Outlet(s) |
- |
| Interior Outlet(s) |
- |
Vehicle-to-Home (V2H)
| V2H via AC Supported |
No |
| Max. Output Power |
- |
| V2H via DC Supported |
Yes |
| Max. Output Power |
7.0 kW DC |
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G)
| V2G via AC Supported |
No |
| Max. Output Power |
- |
| V2G via DC Supported |
Yes |
| Max. Output Power |
7.0 kW DC |
Energy Consumption
EVDB Real Range
| Range |
215 mi |
| Vehicle Consumption |
274 Wh/mi |
| CO2 Emissions |
0 g/km |
| Vehicle Fuel Equivalent |
147 mpg |
WLTP Ratings
| Range |
239 mi |
| Rated Consumption |
298 Wh/mi |
| Vehicle Consumption |
247 Wh/mi |
| CO2 Emissions |
0 g/km |
| Rated Fuel Equivalent |
136 mpg |
| Vehicle Fuel Equivalent |
164 mpg |
Rated = official figures as published by manufacturer. Rated consumption and fuel equivalency figures include charging losses.
Vehicle = calculated battery energy consumption used by the vehicle for propulsion and on-board systems.
NOTE: The fuel equivalency figures are shown in IMPERIAL MPG. Figures in US MPG will differ significantly.
Real Energy Consumption between 187 - 393 Wh/mi
| City - Cold Weather |
281 Wh/mi |
| Highway - Cold Weather |
393 Wh/mi |
| Combined - Cold Weather |
328 Wh/mi |
| City - Mild Weather |
187 Wh/mi |
| Highway - Mild Weather |
303 Wh/mi |
| Combined - Mild Weather |
241 Wh/mi |
Indication of real-world energy use in several situations. Cold weather: 'worst-case' based on -10°C and use of heating. Mild weather: 'best-case' based on 23°C and no use of A/C. For 'Highway' figures a constant speed of 70 mph is assumed. The energy use will depend on speed, style of driving, climate and route conditions.
Safety (Euro NCAP)
| Safety Rating |
|
| Adult Occupant |
93% |
| Child Occupant |
86% |
| Rating Year |
2018 |
| Vulnerable Road Users |
71% |
| Safety Assist |
71% |
For more details on the safety rating of this vehicle, visit
euroncap.com
Dimensions and Weight
| Length |
4490 mm |
| Width |
1788 mm |
| Width with mirrors |
No Data |
| Height |
1545 mm |
| Wheelbase |
2700 mm |
| Weight Unladen (EU) |
1756 kg |
| Gross Vehicle Weight (GVWR) |
2140 kg |
| Max. Payload |
459 kg |
| Cargo Volume |
420 L |
| Cargo Volume Max |
1161 L |
| Cargo Volume Frunk |
No Data |
| Roof Load |
35 kg |
| Tow Hitch Possible |
No Data |
| Towing Weight Unbraked |
0 kg |
| Towing Weight Braked |
0 kg |
| Vertical Load Max |
No Data |
Miscellaneous
| Seats |
5 people |
| Isofix |
Yes, 3 seats |
| Turning Circle |
10.6 m |
| Platform |
No Data |
| EV Dedicated Platform |
No Data |
| Car Body |
Hatchback |
| Segment |
Small Family Car |
| Roof Rails |
No |
| Heat pump (HP) |
Yes |
| HP Standard Equipment |
Yes |
Company Car Tax Indication
Financial Year 2019-20
| BIK Tax Rate |
1% |
| P11D Value from |
£32,890 |
| Benefit in Kind (BIK) |
£329 |
| BIK @ 20% |
£5 pcm |
| BIK @ 40% |
£11 pcm |
| BIK @ 45% |
£12 pcm |
Financial Year 2020-21
| BIK Tax Rate |
1% |
| P11D Value from |
£32,890 |
| Benefit in Kind (BIK) |
£329 |
| BIK @ 20% |
£5 pcm |
| BIK @ 40% |
£11 pcm |
| BIK @ 45% |
£12 pcm |
Financial Year 2021-22
| BIK Tax Rate |
1% |
| P11D Value from |
£32,890 |
| Benefit in Kind (BIK) |
£329 |
| BIK @ 20% |
£5 pcm |
| BIK @ 40% |
£11 pcm |
| BIK @ 45% |
£12 pcm |
* = estimated value. Average energy consumption and range based on moderate drive style and climate. Real-life values may differ significantly. Pricing information might not be actual for some regions. No rights can be derived from the information on this site.



 Nissan Leaf e+
Nissan Leaf e+